P2. Matter & Forces
| Sample chapter matter & forces | |
| File Size: | 789 kb |
| File Type: | |
2.1 Mass and Weight
|
|
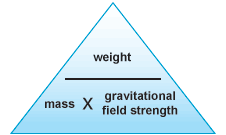
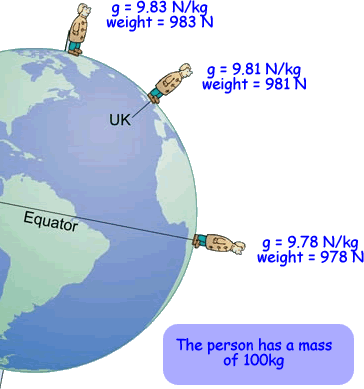
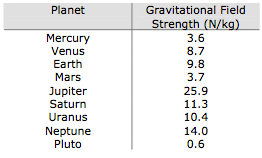
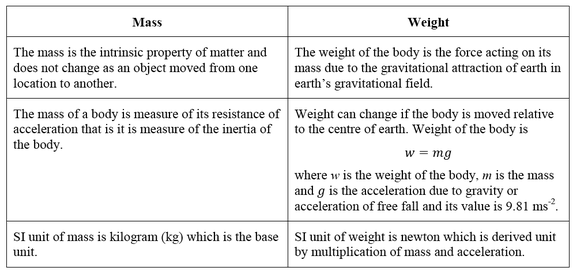
Weight is not the same as mass. Mass is a measure of how much stuff is in an
object. Weight is a force acting on that stuff. Weight is the result of gravity. The Earth's gravity attracts objects towards the centre of the Earth and you feel forces like this as weight. weight = mass × gravity Weight is measured in newtons, N Mass is measured in kilograms, kg The gravitational field strength is measured in newtons per kilogram, N/kg or m/s2 'g' is the gravitational field strength - the force with which gravity pulls each kilogram of mass.This is roughly the same value at the surface of the Earthat all points. It is 9.8 N/kg (to 2 s.f.) |
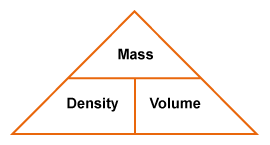
2.2 Density
|
|
Density is a physical property of a substance. At any given temperature and pressure the density of a material is constant. Density is related to two attributes: mass and volume. This gives rise to the formula:
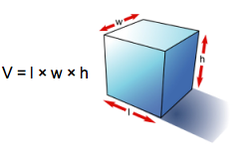
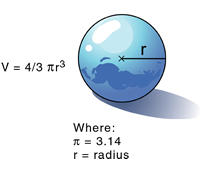
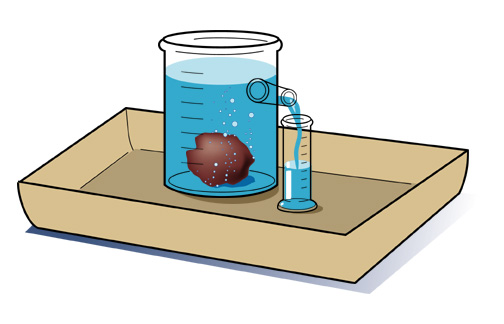
In a laboratory it is possible to determine the mass of an object using a balance. It is also easy to determine the volume of a material; for example, a graduated cylinder can be used to find the volume of a liquid. The volume of a regularly shaped solid can be determined mathematically. It gets a little trickier to determine the volume of an irregular solid; you have to use displacement of water (Archimedes Principle) to find the volume.
Density is typically expressed in grams / cubic centimeter (g/cm3). Equal volumes of different liquids do not necessarily have the same mass. You can demonstrate this by setting up the following situation. All you need are equal volumes of water and corn oil (less dense than water) or corn syrup (more dense than water). The volume of an irregular solid, such as a stone, can be determined by displacement of water. Fill an overflow can so that the water is just above the level of the spout and plug the spout with your finger. Place the overflow can on the counter with its spout above a sink or put the can in a catch basin, uncover the spout and allow the excess water to flow out. Now position a graduated cylinder under the over-flow spout to catch the water that will flow out. Carefully drop the irregularly shaped object into the can and catch the overflowing water in the cylinder. Read the volume of water collected in the graduated cylinder using the markings on the side. The volume of water in the cylinder is equal to the volume of the object. |
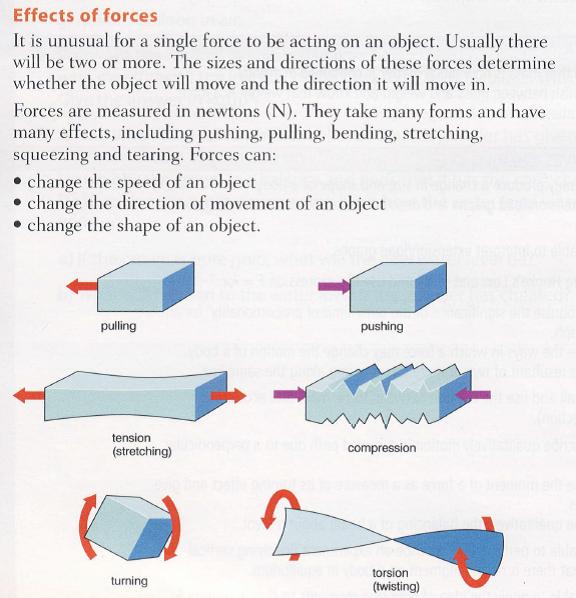
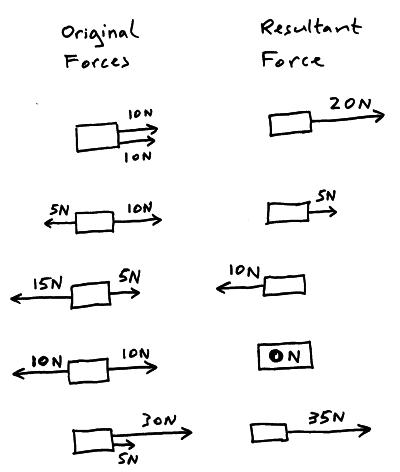
2.3 Effects of forces
Hooke's Law
| Hooke's Law Practical.pdf | |
| File Size: | 32 kb |
| File Type: | |
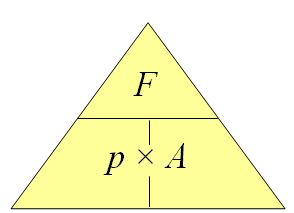
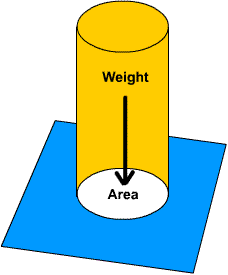
2.4 Pressure
An office table has a weight of 600N. If the area of the base is 3.0 sq metres, what is the pressure on the floor of the office?
This question is dead simple. Simply take the Force (600N) and divide by the area (3.0 sq metres) to get
600N/3 sqmetres
=200 Pa
This question is dead simple. Simply take the Force (600N) and divide by the area (3.0 sq metres) to get
600N/3 sqmetres
=200 Pa
Pressure Exerted by a Solid Iron Cuboid on Sand
Revision
Forces and their effects revision site
Newton’s Laws of Motion revision site
Density & Pressure revision site
Newton’s Laws of Motion revision site
Density & Pressure revision site