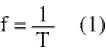P7. Waves
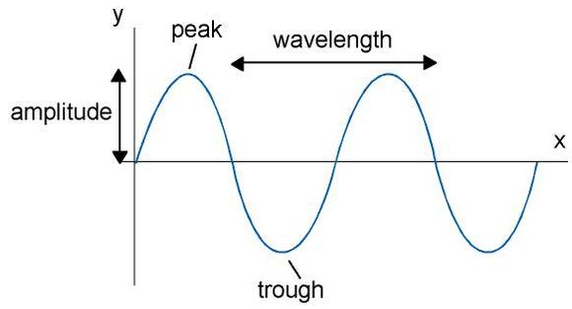
Amplitude
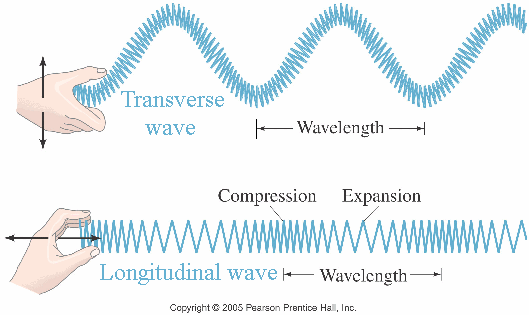
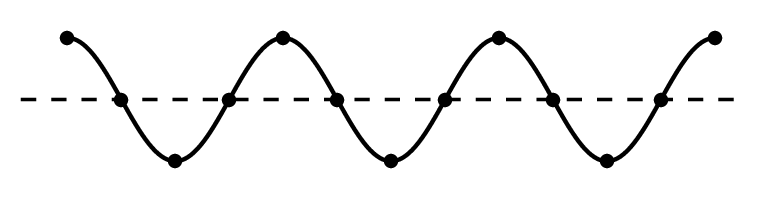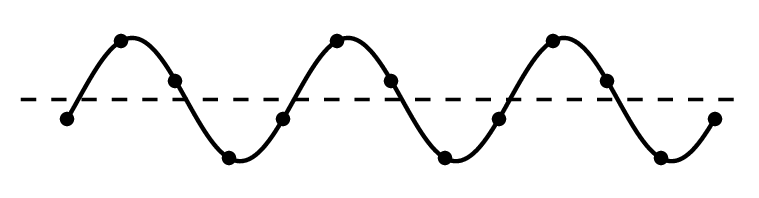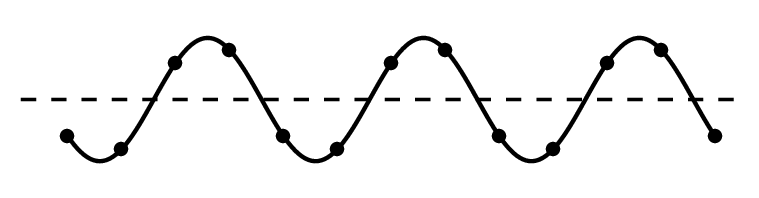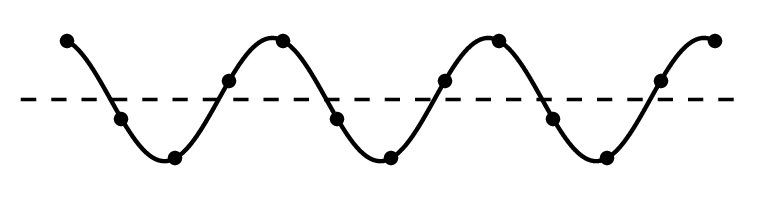
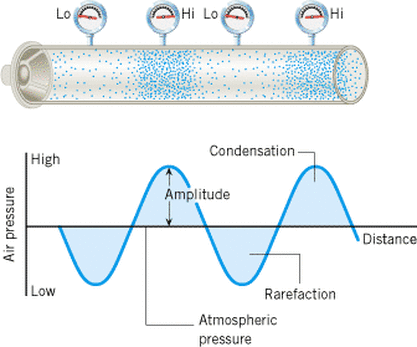
As waves travel, they set up patterns of disturbance. The amplitude of a wave is its maximum disturbance from its undisturbed position. Take care, the amplitude is not the distance between the top and bottom of a wave.
Wavelength
The wavelength of a wave is the distance between a point on one wave and the same point on the next wave. It is often easiest to measure this from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next wave, but it doesn't matter where as long as it is the same point in each wave.
Frequency
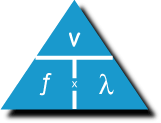
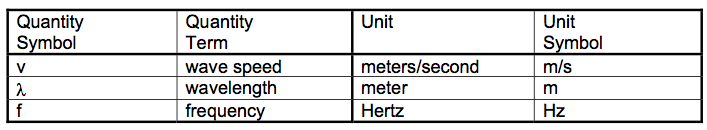
The frequency of a wave is the number of waves produced by a source each second. It is also the number of waves that pass a certain point each second. The unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz).
As waves travel, they set up patterns of disturbance. The amplitude of a wave is its maximum disturbance from its undisturbed position. Take care, the amplitude is not the distance between the top and bottom of a wave.
Wavelength
The wavelength of a wave is the distance between a point on one wave and the same point on the next wave. It is often easiest to measure this from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next wave, but it doesn't matter where as long as it is the same point in each wave.
Frequency
The frequency of a wave is the number of waves produced by a source each second. It is also the number of waves that pass a certain point each second. The unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz).
Types of waves
Transverse Waves
For transverse waves the displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. A ripple on a pond and a wave on a string are easily visualized transverse waves.
For transverse waves the displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. A ripple on a pond and a wave on a string are easily visualized transverse waves.
Longitudinal Waves
In longitudinal waves the displacement of the medium is parallel to the propagation of the wave. A wave in a "slinky" is a good visualization. Sound waves in air are longitudinal waves.
In longitudinal waves the displacement of the medium is parallel to the propagation of the wave. A wave in a "slinky" is a good visualization. Sound waves in air are longitudinal waves.
P7.1 General wave properties
Wave motion and energy
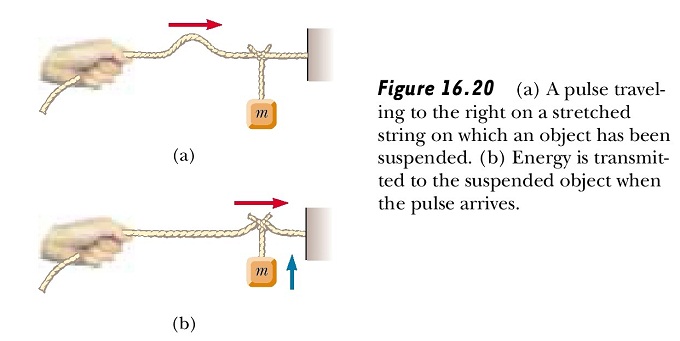
As waves propagate through a medium, they transport energy. We can easily demonstrate this by hanging an object on a stretched string and then sending a pulse down the string, as shown in Figure 16.20. When the pulse meets the suspended object, the object is momentarily displaced, as illustrated in the figure below. In the process, energy is transferred to the object because work must be done for it to move upward.
As waves propagate through a medium, they transport energy. We can easily demonstrate this by hanging an object on a stretched string and then sending a pulse down the string, as shown in Figure 16.20. When the pulse meets the suspended object, the object is momentarily displaced, as illustrated in the figure below. In the process, energy is transferred to the object because work must be done for it to move upward.
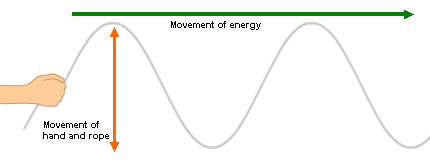
Wave motion is the transfer of energy from one point to another.
- Vibration in ropes: Particles in rope vibrate in a fixed position and energy in the particles are transferred from one end of the rope to the other end. Wave travels as a “sideway pulse”
- Water ripples: An object that is floating experiences both “up and down” motions.
|
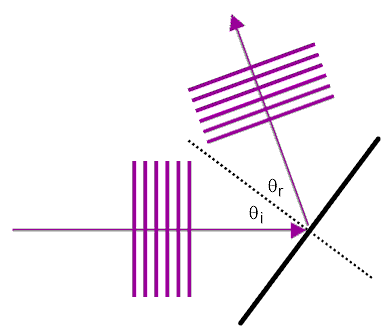
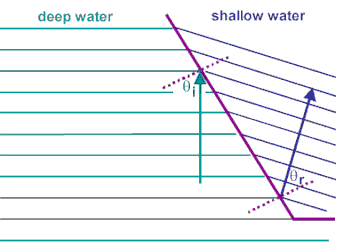
θi is the angle of incidence measured from the normal. θr is the angle of reflection measured from the normal. All waves obey this relationship that θi = θr Refraction is the bending of a wavefront resulting from a change in wave speed. This occurs when there is an abrupt change in the medium through which the waves are traveling. Notice that during the refraction of plane waves across an oblique interface, neither the frequency nor wave shape change. However, the wavelength decreases in the slower medium, the shallow water. This decrease is caused by a reduction in the wave's speed. |
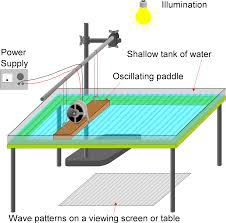
Practical Work- Ripple Tank
|
A ripple tank is a shallow glass tank of water used in schools and colleges to demonstrate the basic properties of waves. The ripple tank is usually illuminated from above, so that the light shines through the water. The ripples on the water show up as shadows on the screen underneath the tank. All the basic properties of waves, including reflection, refraction, interference and diffraction, can be demonstrated.
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||